Choosing a Computer
These are some helpful PC component requirements depending on what you plan on using your computer for. These are only NB's recommendations, your specific needs may vary.
* photography, art, video editing
size:
27"- 32" (video)
resolution:
processor (speed):
4 GHz >
memory (RAM):
storage (hard drive):
SSD: 500GB >
size:
resolution:
processor (speed):
4 GHz >
memory (RAM):
storage (hard drive):
SSD: 1TB >
size:
resolution:
processor (speed):
3 GHz >
memory (RAM):
storage (hard drive):
SSD: optional
size:
teens: 13" >
teachers: 24" - 27"
resolution:
processor (speed):
3 GHz >
memory (RAM):
storage (hard drive):
SSD: optional
size:
portable: 13" - 17"
resolution:
processor (speed):
3 GHz >
memory (RAM):
storage (hard drive):
SSD: optional
operating system
dedicated GPU (graphics card)
portable
popular pc brands
SEE BELOW
wifi
battery life
- the brightness of your display
- large number of peripherals / unpowered peripherals
- running heavy applications / programs running in the background
- too many network (wifi) connections
- your old battery needs replacing
- overheating your laptop (bad for all components) / blocking air vents
peripherals
- mouse
- stylus pen
- keyboard
- webcam
- microphone
- monitor
- speakers
- projector
- printer
- USB Flash Drive / SD cards
- external hard drive (HDDs, SSDs)
warranty / protection plan
Popular PC Brands
These are just suggestions based on many "best of" lists from 2022 researched. It\'s still recommended to do your own research based on your needs!
Acer, Gigabyte Aero, HP Pavilion Gaming Desktop, MacBook Pro
Do you want it portable? Go for a convertable laptop. Some highly rated include:
HP Spectre X360, Dell XPS or Latitude, Lenovo (various models),
Acer Chromebook, Microsoft Surface Laptop Studio or Surface Pro, HP EliteBook X360, Samsung Galaxy Book Flex, Panasonic Toughbook 33
Acer, Alienware, Corsair, Dell (models dedicated to gaming), HP Omen, iBuyPower, Lenovo, Maingear, MSI, Origin
Acer, Apple, Dell, HP, Lenovo, Microsoft
What is HDD and SSD storage?
Simply put, HDDs are mechanical units built inside of a PC and best for storing data. SSDs, on the other hand, are non-mechanical, often external storage devices that are best for running games, apps, and videos. SSDs are usually more expensive than HDDs.
Notable Events
Ah, computers. What would the modern world be like without computers? How many friends or family are you in contact with because of a social media platform you use on a computer?* How many of those friends and family have you not even meet in person? How about the millions of Zoom (communications platform) users out there being able to hold down a job simply because they can show up on time in front of their computer? It's undeniable how important computers are in all countries economically but it's essential in our connection to not only our friends and family but the whole world.
* your phone is a computer| c.2500BC | The abacus, the first known calculator, was invented |
| c.500BC | The Ashtadhyayi, a list of grammar rules for Sanskrit, was created by Pānini, inspiring formal language theory |
| c.200BC | Pingala develops a binary system similar to Morse code in which he used light (laghu) and heavy (guru) markings rather than 0s and 1s. |
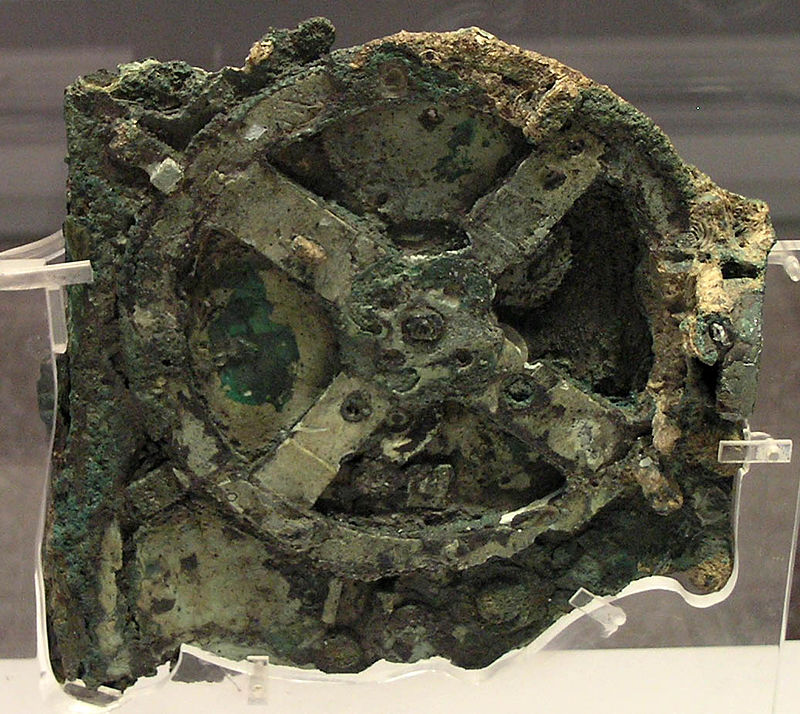
| c.205BC - c.87BC | The first known mechanical analogue computer, the Antikythera was invented |
| 725AD | The world’s first mechanical clock was invented by Liang Lingzan (the earliest computers used technology based on clocks) |
| c.1450 | Kerala School of Astronomy and Mathematics invents the floating-point number system |
| 1642 | Blaise Pascal invents the mechanical calculator |
| 1666 | Sir Samuel Morland creates an adding machine |
| 1672 | Gottfried Wilhelm von Leibniz invents the Step Reckoner calculator, capable of multiplication |
| 1689 | The modern binary number system, the basis for binary code, was invented by Gottfried Wilhelm von Leibniz |
| 1774 | Philipp Matth äus Hahn creates a calculator capable of calculating the four mathematical operations |
| 1804 | Invention of the Jacquard machine ("Jacquard loom") by Joseph Marie Jacquard |
| 1822 | Charles Babbage invents an automatic mechanical calculator capable of tabulating polynomial functions |
| 1831 | Giovanni Antonio Amedeo Plana invents the perpetual calendar machine |
| 1835 | The invention of the Electromechanical Relay by Joseph Henry |
| 1843 | Charles Babbage starts the design of his Analytical Engine, an early mechanical computer |
| 1847 | George Boole develops Boolean algebra |
| 1866 | The first practical logic machine, the logical abacus, was developed by William Stanley Jevons |
| 1884 | The first commercially successful key-driven mechanical calculator was developed by Dorr E. Felt |
| 1886 | Charles Sanders Peirce conceived of the idea of logical operations being carried out by electrical switching circuits |
| 1887 | Serbian-American engineer and physicist, Nikola Tesla, invents the first alternating current (AC) motor |
| 1890 | The electromechanical punched card tabulator, a machine designed to assist in summarizing information stored on punched cards, was invented by Herman Hollerith |
| 1899 | NEC Corporation, an IT company, is founded |
| 1904 | The diode (vacuum tube) was invented by John Ambrose Fleming |
| 1906 | The Audion (vacuum tube), the first triode, was invented by Lee de Forest |
| 1911 | International Business Machines Corporation ("IBM") was founded (first as Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company "CTR") |
| 1919 | The first flip-flop (latch) design, was published by William Henry Eccles and Frank Wilfred Jordan |
| 1934 | Akira Nakashima introduces switching circuit theory |
| 1936-1937 | The Universal machine (Universal Turing machine - "UTM") was conceived by Alan Turing |
| 1936-1938 | Invention of the first programmable computer, the Z1, by Konrad Zuse |
| 1939 | The Hewlett-Packard Company (HP) was founded |
| 1939-1942 | Invention of the first automatic electronic digital computer, the Atanasoff–Berry computer ("ABC"), by John Vincent Atanasoff and Clifford Berry |
| Samuel Williams and George Stibitz complete the Complex Number Calculator ("Model I Relay Calculator"), capable of calculating complex numbers | |
| 1942 | The S2, the first process computer, was created by Konrad Zuse |
| 1942-1945 | The first high-level programming language, Plankalkül, designed for engineering purposes by Konrad Zuse |
| The Von Neumann architecture ("Von Neumann model", "Princeton architecture") conceived by John von Neumann | |
| 1946 | The first electronic general-purpose computer, the ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), was designed by John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert |
| 1947 | Invention of the first transistor by William Shockley, John Bardeen, and Walter Brattain at Bell Laboratories |
| 1948 | The Manchester Baby (Small-Scale Experimental Machine - "SSEM"), the first electronic stored-program computer, ran its first program |
| 1950 | Alan Turing publishes Computer Machinery and Intelligence, a paper on artificial intelligence including what's known as the Turing Test, a machine's capability of thinking like a human being |
| 1951 | Whirlwind, the first real-time 16-bit computer, was built |
| The CSIRAC, the first computer to play digital music, was publicly displayed | |
| The United States Census Bureau uses the first commercial computer, the UNIVAC I (Universal Automatic Computer), designed by John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert | |
| 1953 | The University of Manchester complete the first transistorized computer |
| The first mass-produced computer, the IBM 650, was introduced | |
| 1954 | The first commercially available programming language, FORTRAN (Formula Translation), developed by a team led by John Backus at IBM |
| 1955 | Gregorio Zara creates the first videophone |
| 1957 | The first non-impact dot printer was released by IBM |
| 1958 | The first successful working example of the integrated circuit by Texas Instruments was released |
| Bell Labs researchers invent the modem | |
| c.1960 | Paul Baran develops the concept of packet switching |
| 1961 | The Compatible Time-Sharing System ("CTSS") became the first computer capable of instant messaging |
| 1962 | The Atlas, the first computer to have virtual memory, is completed |
| 1963 | The computer mouse is conceived by Douglas Engelbart |
| The first universal standard for computers, ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Exchange), is developed | |
| IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers), pronounced Eye-triple-E, was founded. IEEE is a professional association and the world's largest association of technical professionals who is dedicated to the advancement of technology for the benefit of humanity. | |
| 1965 | Moore's Law, by Gordan Moore, was published |
| The programming language, BASIC, was developed | |
| Lawrence Roberts & Thomas Marill create the first Wide-area Network ("WAN") | |
| 1966 | The ARPAnet project initiates, laying the foundation for today’s Internet |
| 1967 | The first real-time visual flight simulator was developed by Danny Cohen |
| The floppy disk is invented by Alan Shugart | |
| 1968 | Intel, an American multinational corporation and technology company, is founded |
| The first scientific calculator, HP's HP-9100A, was released | |
| 1969 | UNIX operating system is developed |
| 1970 | The first dynamic RAM chip is introduced by Intel |
| 1972 | The programming language, C, is developed at Bell |
| 1973 | The TCP/IP (internet protocols) is developed |
| The Ethernet is developed | |
| IBM's SCAMP computer, considered to be the first personal computer, was released | |
| 1974 | Nicholas K. Sheridon produced the first flexible e-paper display, paving the way for electronic visual displays for future devices |
| 1975 | MITS' Altair 8800, recognized as the first commercially successful personal computer, was released |
| Microsoft,an American multinational technology company, is founded | |
| The first computer with a single-boarded circuit board, the Micron-1, was released | |
| 1976 | Apple, an American multinational technology company , is founded |
| Acer, a Taiwanese multinational hardware and electronics corporation, is founded | |
| The first laser printer, by IBM, was released | |
| 1978 | Intel releases the first x86 microprocessor |
| 1979 | The compact disc is invented |
| 1980 | The first single-chip, fully 32-bit processor, the Bellmac 32, was produced |
| 1981 | The first commercially successful portable computer, the Osborne I, was released |
| Richard Feynman conceived of quantum computers | |
| Apple's Lisa computer is the first commercial computer to use a WIMP (Windows, Icons, Menus, and Pointing Devices) paradigm | |
| 1982 | Compaq, an American computer and computer supply company, was founded (Compaq was acquired for by HP in 2002) |
| 1983 | Microsoft program Word was released |
| Paul Mockapetris invents the Domain Name System | |
| The first 3D printed part ("3D printer") was created by Chuck Hull, who is often called the "Father of 3D Printing" | |
| 1984 | Dell, an American multinational computer technology company, is founded |
| The Macintosh System I, the first version of Classic Mac OS (an operating system), was released on the first of Macintosh's personal computers, the Macintosh 128K (originally releases as Apple Macintosh) | |
| 1985 | The first domain name, Symbolics.com, was registered |
| The first release of Microsoft's Windows OS (Windows 1) | |
| 1988 | The first optical chip (for fiber-optic communication) was developed |
| Adobe Photoshop was created by Thomas and John Knoll | |
| 1989 | Tim Berners-Lee invents the World Wide Web information system and scripting language HTML |
| The first "notebook" (ie. laptop computer), the Ultralite, was released by NEC | |
| 1990 | Microsoft program Office was released |
| The first web browser, World Wide Web (later named Nexus), developed by Tim Berners-Lee, was released | |
| 1991 | The Linux Kernel (an operating system) was released |
| 1994 | The first proper "smartphone", the IBM Simon Personal Communicator ("IBM Simon"), was released |
| 1995 | Java programming language, created by James Gosling, was released |
| JavaScript (a scripting language) was developed by Brendan Eich | |
| The Internet Explorer browser was released | |
| 1997 | IBM's Deep Blue becomes the first computer to beat a world chess champion |
| 1998 | Google, an American multinational technology company, is founded |
| 1999 | The term Wi-Fi was commercially used, coined by the brand-consulting firm Interbrand |
| 2001 | Wikipedia, a free online encyclopedia hosted by the Wikimedia Foundation, launches |
| 2003 | The first 64-bit x86 processor, AMD's Opteron, was released |
| Skype, a telecommunications application, was released | |
| 2004 | Mozilla's Firefox browser was released |
| 2005 | YouTube, an American video-sharing website, launches |
| 2007 | The first Apple iPhone was released |
| 2008 | Google's Chrome browser was released |
| The first version of Google's Android mobile operating system was released on the HTC Dream Phone | |
| 2009 | Bitcoin cryptocurrency was released |
| 2010 | Apple releases the first iPad |
| 2012 | The Raspberry Pi was released |
| 1QBit, a quantum computing software company, was founded | |
| 2015 | NASA displays the first fully operational quantum computer |
| Discord, a communication service featuring private servers, first launches | |
| 2018 | Royole releases FlexPai, first commercial foldable smartphone with flexible display that also transforms into a tablet |
| 2019 | The IBM Q System One, the first commercially available circuit-based quantum computer, is introduced |
| The first folding smartphones are introduced with Samsung introducing the Galaxy Fold and the Huawei Mate X from Huawei | |
| Google begins drone based delivery service via Google Wing in select areas | |
| 5G networks service in America began | |
| 2021 | a British patient named Steve Verze received the world's first fully 3D-printed prosthetic eye |
| NFT sales total roughly $24.9 billion | |
| DALL-E, a text-to-image model developed by OpenAI, was released | |
| 2022 | OpenAI launches ChatGPT , an AI language model designed to assist with natural language processing tasks. |
| Midjourney, a text-to-image model, became available as an open beta | |
| Stable Diffusion, another text-to-image model, was released | |
| LangChain, an app-creating framework that used LLMs (Large Language Models), was released | |
| Google started Project Green Light, a traffic analyzing program | |
| 2023 | The AI(Artificial Intelligence) PC was introduced |
| IBM released the first-ever 1,000-qubit quantum chip, Condor | |
| 2024 | Elon Musk announced that the first human had received an implant from Neuralink |
| An AI powered robot called Ai-Da created a painting of Alan Turing called "AI God: Portrait of Alan Turing" that sold for $1.08 million | |
| Google introduced the smart glasses platform Google XR | |
| 2025 | Microsoft unveiled its first quantum computing chip, called the Majorana 1 |
| Microsoft announced it would be shutting down Skype |
Terms
3D print(er/ed) : The construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model.
algorithm: An algorithm is an ordered and finite set of operations (instructions) that must be followed in order to solve a problem. An algorithm takes a user’s input and generates an output based on its set of instructions. When a developer creates a program, he is essentially creating a set of algorithms.
alternating current (AC) motor : An AC motor is an electric motor driven by an alternating current (AC). The AC motor commonly consists of two basic parts, an outside stator having coils supplied with alternating current to produce a rotating magnetic field, and an inside rotor attached to the output shaft producing a second rotating magnetic field. - Wikipedia
binary number system : An alternative to the decimal (10-base) number system that we use every day. Binary numbers are important because using them instead of the decimal system simplifies the design of computers and related technologies. The simplest definition of the binary number system is a system of numbering that uses only two digits—0 and 1—to represent numbers, instead of using the digits 1 through 9 plus 0 to represent numbers. - ethw.org
BIOS: Modern computers have to rely on an operating system to work. The operating system is loaded once the computer is turned on. Once the computer is turned on it loads the operating system through a booting process.
The BIOS (Basic Input / Output System) is software (mostly on Windows operating systems) that allows the CPU to initialize, test the system input and output components, and load the operating system. It is part of the booting process and the first software to run when the computer is powered on.
Other computer operating systems might rely on other software besides BIOS for this booting process.
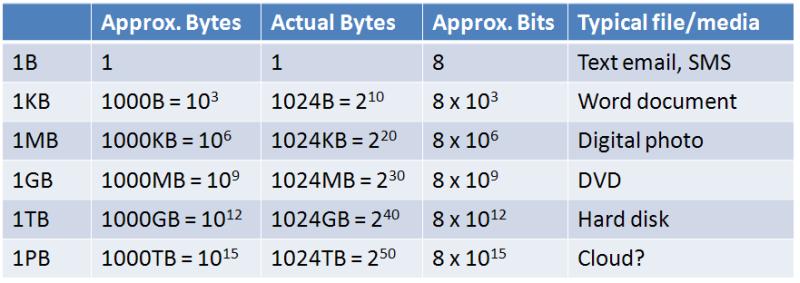
bit : A bit (short for binary digit) is the smallest unit of data in a computer. A bit has a single binary value, either 0 or 1. In most computer systems, there are eight bits in a byte. For example: 1 bit at its simplest is an answer to a yes or no question. 1 byte is a number from 0 to 255, 8 and 16GB are the two most common sizes of USB flash drives, and 16TB, as of 2018, was the largest commercially available solid state drive sold.
Boolean algebra : Boolean Algebra is used to analyze and simplify the digital (logic) circuits. It uses only the binary numbers i.e. 0 and 1. It is also called Binary Algebra or logical Algebra. - tutorialspoint.com
boot: Booting a computer refers to the process of powering on the computer and starting the operating system.
cache: Cache (pronounced like "cash") is where recently-used information is placed where it can be accessed faster. Common types of caches include browser cache, disk cache, memory cache, and processor cache but they’re most commonly used in web browsers. For example, Google Chrome uses a cache to store the pages, images, and URLs of recently visited websites allowing for faster download the next time you visit.
CAD (Computer-aided design): A software to help engineers, artists, etc. with the production of their products, inventions, etc.. The software is also helpful in protecting said products and inventions when used in patent applications.
ChatGPT (Chat Generative Pre-Trained Transformer) : A chatbot that works by following patterns developed by analyzing the text it has gathered from the Internet among other sources. A user can ask simple day-to-day questions, recipes, coding questions, even full essays!
clock speed:clock speed is the operating speed of a computer or, more specifically, its microprocessor's speed expressed in cycles per second. It is typically measured in megahertz (equal to one million cycles per second) or gigahertz (equal to 1billion cycles per second). In general, the higher the CPU speed, the better a computer will perform.
compact disc : Originally developed to store and play only sound recordings (CD-DA) the compact disc was later adapted for storage of data (CD-ROM),typically storing up to 700 MiB (apx. 734 MB) of data.
CPU...See also microprocessor : The CPU (central processing unit) can be considered the most important element of a computer system. The CPU is the brain of the computer performing the basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output (I/O) operations specified by its instructions. The two typical components of a CPU include the arithmetic logic unit (ALU), which performs arithmetic and logical operations and the control unit (CU), which extracts instructions from memory and decodes and executes them. Most modern CPUs are microprocessors, meaning they are contained on a single integrated circuit (IC) chip causing the two terms to be synonymous.
cryptocurrency : A cryptocurrency (or crypto currency) is a digital asset designed to work as a medium of exchange that uses strong cryptography to secure financial transactions, control the creation of additional units, and verify the transfer of assets. Cryptocurrencies use decentralized control as opposed to centralized digital currency and central banking systems. ...The underlying technical system upon which decentralized cryptocurrencies are based was created by the group or individual known as Satoshi Nakamoto. - Wikipedia
Deepfake(s): Deepfakes are synthetic media techniques that uses machine learning and artificial intelligence to manipulate or generate visual and audio content to replace one person's likeness convincingly with that of another.
disk drive: The term disk drive is a general term that describes a device that reads and/or writes data to a disk.

Electromechanical Relay : Electromechanical relays are used in many of today's electrical machines when it is vital to control a circuit, either with a low power signal or when multiple circuits must be controlled by one single signal. - relays.weebly.com
Ethernet : Ethernet is the technology that is most commonly used in wired local area networks (LANs). A LAN is a network of computers and other electronic devices that covers a small area such as a room, office, or building. - lifewire.com
fiber-optic : Optical fiber (a very thin, flexible, transparent fiber made of silica or plastic) bundled as cables is commonly used as a medium for telecommunication and computer networking through what's called "Fiber-optic communication".
flip-flop (latch) : a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information
floating-point number system : Floating-point representation is similar in concept to scientific notation. Logically, a floating-point number consists of: A signed (meaning positive or negative) digit string of a given length in a given base (or radix). - ethw.org
floppy disk : a type of disk composed of a thin magnetic storage medium inside a rectangular plastic enclosure whose popular use was as a storage unit for storing data for personal computers, similar to the use of USB flash drives in modern computing
formal language theory : The field of formal language theory studies primarily the purely syntactical aspects of such languages—that is, their internal structural patterns. - Wikipedia Computer Scientists have discovered good ways to write programs that process other programs, and a key ingredient is that you have to specify what is allowed in a program very precisely. That's where formal languages come in. - csfieldguide.org.nz
integrated circuit : An integrated circuit is a chip, usually made of silicon, holding or "integrated" inside such electronic components such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, etc.. The integrated circuit is created out of a single piece of silicon whereas a discrete circuit's components are made separately from different materials and often assembled later.
IT : stands for "Information Technology" and refers to anything related to computing technology: networking, hardware, software, and general trouble-shooting
Jacquard machine ("Jacquard loom") : The Jacquard machine is a device fitted to a power loom that simplifies the process of manufacturing textiles with such complex patterns as brocade, damask and matelassé. - Wikipedia
laser printer : Laser printers produce high-quality images by passing a laser beam back and forth over a negatively charged cylinder called a drum. The drum then collects electrically charged powdered ink (toner), and transfers the image to paper, which is then heated to permanently fuse the image. Laser printers use the same basic technology as photocopiers except whereas the photocopier already has an original image, it just copies it, the laser printer has to write out an image from scratch, converting the electronic data into an image.
microprocessor (processor) ...See also CPU : The microprocessor (processor) is a multipurpose, clock driven, register based, digital integrated circuit that accepts binary data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory and provides results as output. - Wikipedia
Microprocessors, considered the brains of and most important element of a computer, are capable of many functions, such as word processing, calculation, and communication via Internet, telephone and to other parts of the device it’s contained in.
Everything a computer does is described by instructions of computer programs, and microprocessors carry out these instructions many millions of times a second.
modem : A modem, or modulator demodulator, is used to communicate between distant computers. modulation is the changing of the digital data from a computer into analog data be sent over telephone lines and demodulation is the changing of the analog data which is received over the telephone lines to digital data to be used by the computer.
Moore\'s Law : Moore's Law is the principle that the speed and capability of computers can be expected to double every two years, as a result of increases in the number of transistors a microchip can contain.
NFT : A non-fungible token is an asset that has been tokenized via a block chain. NFTs can represent digital or real-world items like artwork and real estate. Technically, the first NFT was designed back in 2014 by Kevin McKoy but since than has grown in popularity.
operating system : An operating system is in charge of many things. Among them are to make sure that all the programs can use the CPU (central processing unit), system memory, displays, input devices, and other hardware. Some also give the user an interface to use the computer via WIMPs (Windows, Icons, Menus, and Pointing Devices).
packet switching : Packet switching is the approach used by computer network protocols to deliver data across a local or long-distance connection via a router(s).
In Packet switching, a message ("data") is broken into a number of parts ("packets") at the source which are sent independently, over the best available route for each packet, and reassembled at the destination.
programming language : A programming language is a vocabulary and set of grammatical rules for instructing a computer or computing device to perform specific tasks.
quantum computer : A quantum computer is a computer which makes use of the quantum states of subatomic particles to store information.
Quantum computers take advantage of the ability of subatomic particles to exist in more than one state at any time and due to the way the particles behave, operations can be done much more quickly and use less energy than conventional computers.
RAM : RAM (Random Access Memory) is the hardware in a computing device and type of data storage where the data in current use are kept. Its memory is volatile and all information that was stored in RAM is lost when the computer is turned off.
Raspberry Pi : The Raspberry Pi is a small, affordable computer. It provides a set of GPIO (general purpose input/output) pins for electronic components and enables people of all ages to explore computing. It’s a great tool for learning how to code and can be used for a range of tasks and creations.
scripting language : Scripting languages are commonly used today in web design, adding functionality to a web page such as different menu styles, graphic displays, and simple animations. While static content on a web page can be generated by a single HTML document, powerful scripting languages like JavaScript and PHP, can create more dynamic (not static-i.e. dropdown-menus and simple animations) web content.
Steins;Gate : Steins;Gate is a Japanese anime (and site creator’s favorite anime), whose plot revolves around time travel and an IBM 5100 computer (released in 1975, six years before the IBM Personal Computer). The anime has a character, John Titor , who is actually based on a real person said to be a time traveler.
switching circuit theory : Switching circuit theory is the mathematical study of the properties of networks of idealized switches and is essential to telephone, data processing, and other technologies in which it is necessary to make rapid decisions about routing information.
Circuit switching is just one form of data transmission; the other is Packet switching (which especially today is more efficient). The main difference between circuit switching and packet switching is that Circuit Switching is connection oriented whereas, Packet Switching is not.
text-to-image model :A text-to-image model is a machine learning model which takes an input natural language prompt and produces an image matching that description.
transistor : A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material usually with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Today, some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits.
The transistor is the fundamental building block of modern electronic devices, and is ubiquitous in modern electronic systems. - Wikipedia
Universal Machine : The Universal machine (Universal Turing machine) is a theoretical idea which plays an important role in the foundations of mathematics and computer science. It is essentially a Turing machine that is able to simulate any other Turing machine.
A Turing machine in itself consists of an infinitely-long tape which acts like the memory in a typical computer. The machine has a head which is positioned over one of the squares on the tape and in these squares can be written characters, for example a "1" or a "0". Then depending on what it was programmed to do, it then edits the tape one square at a time writing or not writing another character.
Simply put…
1)The machine will first read the symbol under the head
2)write a new symbol accordingly
3)move the tape left or right as instructed
It then keeps repeating this read-write-move sequence again unless we assign the previous set of instructions to a machine state. The machine will perform those instructions when it is in that specified state.
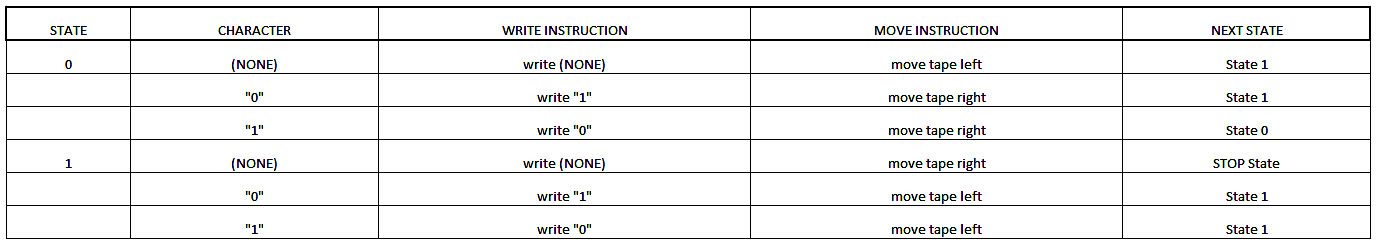
It is also possible to add additional states to the program (as seen above), instructing the Turing machine to perform more complex functions and hence run any algorithm (a process or set of rules to be followed in calculations or other problem-solving operations, especially by a computer).
A Universal Turing machine is special in that it reads both the description of the machine to be simulated as well as the input from its own tape.
vacuum tube : a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied - Wikipedia
virtual memory : Virtual memory is a computer system's secondary and temporary memory storage space. Primary memory is usually stored in the system’s RAM but may become overloaded for a number of reasons and have to use the virtual memory to lighten the load.
Von Neumann architecture : The Von Neumann architecture is a computer architecture based on a description by the mathematician and physicist John von Neumann and others in the First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC ("Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer" - one of the earliest electronic computers).
The document describes design architecture for a computer with three basic units: the Central Processing Unit (CPU), the Main Memory Unit, and the input/output Device.
web browser : A web browser, or "browser," is a software application used to access and view websites. A variety of web browsers are available with different features, the most common are Google Chrome, Microsoft Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, Opera, and Apple Safari.
Wide-area network : A wide area network (WAN) is a telecommunications network usually used for connecting computers over a large-scale geographical area. A WAN connects different smaller networks, including LANs ("local area network" - a group of computers and network devices connected together, usually within the same building) and MANs ("metropolitan area network" - a larger network that usually spans several buildings in the same city or town). The internet is a prime example of a WAN.
Wi-Fi : Wi-Fi is a networking technology which allows a user to connect to a network using radio waves, without needing to use wires. Common uses can include browsing the internet via laptop or smartphone, sharing documents to a computer from a smartphone or another computer, printing documents on a wireless printer, and streaming movies.
